Are AI Detectors Accurate? We tested 3 AI Detectors To Find!

With the advent of AI writers, AI detectors have equally hit the market.
Some universities have been using plagiarism detectors to flag copied content and now they’re jumping on the bandwagon of AI detectors– like Turnitin, Originality.ai, and GPTZero.
A recent survey of 1,000 students by intelligent.com discovered that 30% admitted to using ChatGPT for their assignments.
Some universities have taken action and implemented the tool, while others like the University of Manchester have opted out until they can properly assess its implications for staff and students.
Turnitin– the plagiarism and AI detection tool has been checking around 38 million student essays since its AI detector tool was released in April 2023.
The company has been under heat after saying that the software has a reliability issue than it initially suggested.
Let’s check if the self-acclaimed 97% AI detectors are the real deal or just a misleading commotion.
What is an AI Detector?
A.I. detection is a process used to determine whether the content is generated by artificial intelligence (namely generative AI) or a human.
AI detectors use machine learning and Natural Language Processing (NLP) methods to analyze the word choice and pattern of content.
Content AI detectors can be used for text, images, and videos.
Some commonly used A.I detectors are GPTZero, Turnitin, Winston AI, Originality.ai, and Copy leaks.
AI detectors are mainly used to catch whether an essay was written by a student or a content piece was written by a human. But why? Well, here’s the answer:
- Ensure academic integrity and prevent plagiarism or cheating
- Detect fake news and false information from spreading
- Protect intellectual property and copyright
How do AI Detectors Work?

AI detectors use various methods and criteria to determine whether a piece of content is human-written or not, such as perplexity, burstiness, typos, and other grammatical errors.
Perplexity is the sophistication of a language pattern that informs how unpredictable a text is.
Since AI models aim to produce content with low perplexity and smoother to read, a low perplexity rate indicates AI-generated text.
Human written content has a higher perplexity and creative language choices.
Burstiness is the variation of words or phrases in a length of sentence during a short span.
Since AI models rely on a particular set of data, they tend to use the same words more than needed and are more uniform–causing a low burstiness of text.
Human writing on the contrary varies in terms of words and sentence length.
Let’s give you a rough example of how it’s done
How do you think this sentence should end?
“She loves to play the…”
A human might say “saxophone”, “violin”, or “guitar” as answers, as those words are possible, but they are not very common or specific. It’s a thing.
Humans love to be unique and outward so they’re likely to suggest something that’s “better than anyone”
A language model with low perplexity might answer “piano” or “flute”. Those words are more likely, relevant, and predictable according to the context.
AI detectors like GPTZero compare the perplexity and burstiness of a text to a certain threshold and assign a score or probability of how human-like a text is.
But here’s the catch. These methods are neither efficient nor reliable.
Are A.I Detectors Accurate?
Critics and experts argue that AI cheating will always be possible and dodgy, especially if the models are powerful and large.
They suggest watermarks for AI written content to avoid usage by students and reduce the chances of copying.
Thomas Lancaster–a computer scientist and contract cheating expert at Imperial College London has warned about the latest AI model ChatGPT-4 claiming that it’s very human-like and difficult to point out.
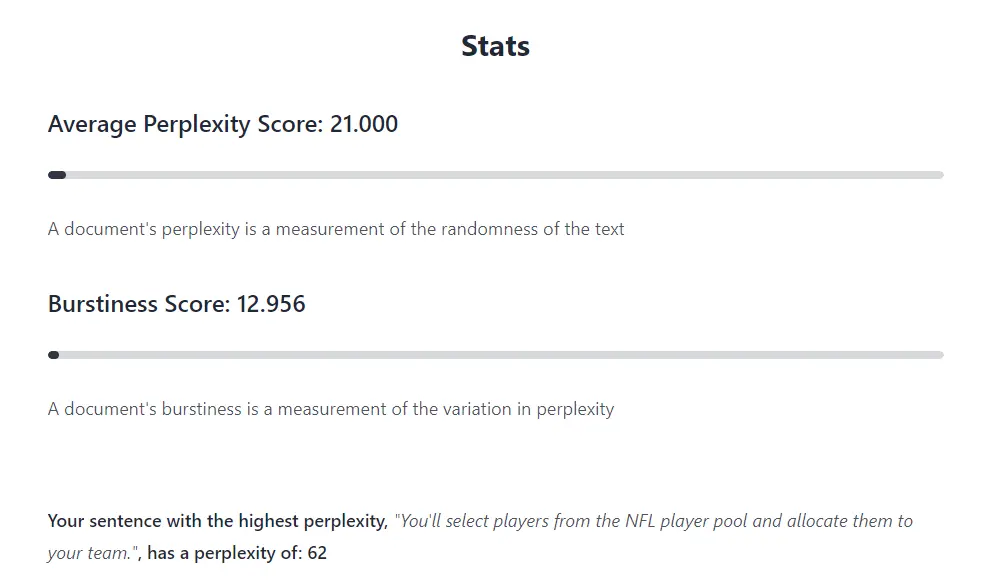
I tested the most used A.I detector GPTZero to check how accurate it is in terms of picking A.I content.
I picked this article and pasted the content in GPTZero and here’s the result.
But here’s the issue. This article was published in 2021 while ChatGPT was released in 2022. Ok? No problem, let’s try another article.
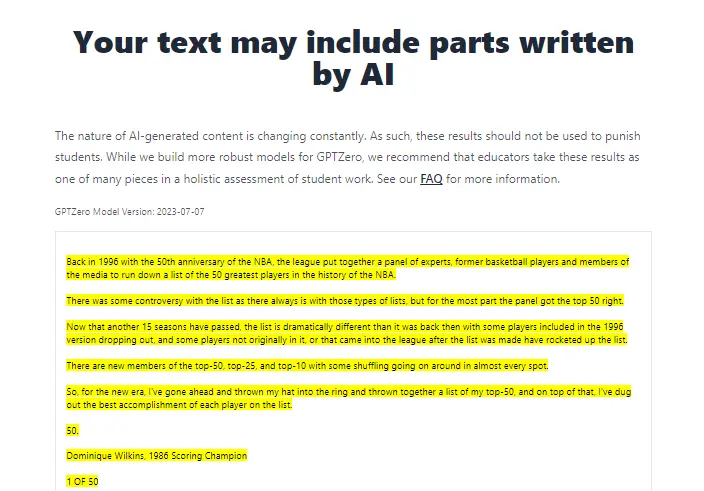
But…This article was published in 2011!
I then tested this article in 3 other A.I detectors. As you can see–GPTZero and ZeroGPT are highly inaccurate and if used in an academic environment, it may just harm the students’ reputation.
Copyleaks and Originality.ai can be marked as 90% accurate because tools can’t be 100% sure.
1. ZeroGpt
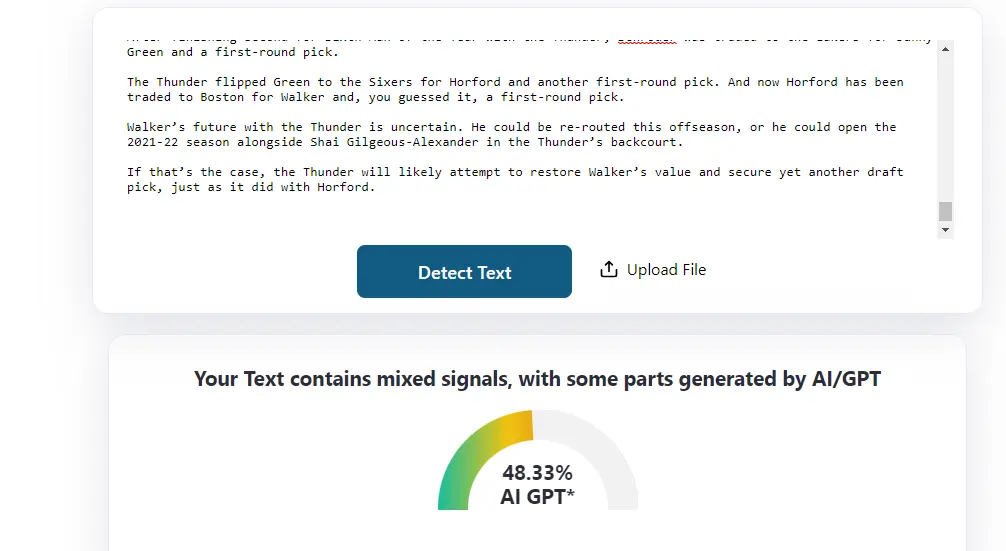
2. Copyleaks
3. Originality.ai
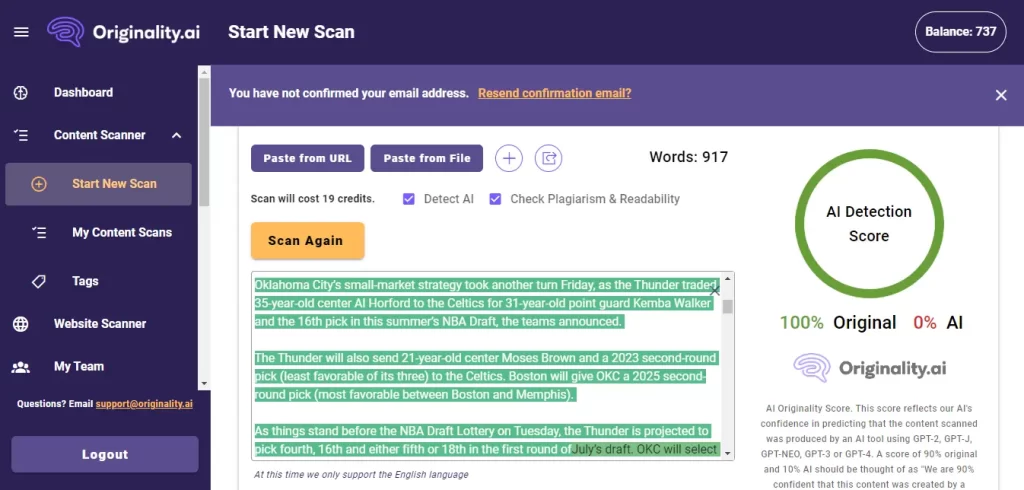
There have been several reported incidents where the students were wrongly flagged for having their assignments mistaken as A.I written.
A Texas A&M University-Commerce professor flunked all his students after ChatGPT falsely claimed it wrote their papers, while a UC Davis student Louise Stivers fell victim when her college rooted out her essays and exams as being completed by chatbots.
When Turitin released its AI detection tool, the company said its technology has less than 1 percent rate of the most problematic kind of error–false positive, where a student’s writing is incorrectly flagged as AI.
Now Turnitin has changed its claim saying the software can incorrectly flag 4% of writing.
Turnitin failed to specify the error rate of documents with 20% AI writing, which can lead to false positives and false negatives.
This may cause disastrous consequences for students who might lose marks or get terminated for going against disciplinary action.
Are AI Detectors Biased?
AI detectors, specifically those designed to identify AI-generated content, have shown a significant bias against non-native English speakers.
This bias manifests in the consistent misclassification of non-native English writing as AI-generated, while accurately identifying native English writing samples.
The underlying mechanism for this bias is the use of “text perplexity” by the detectors which involves predicting the next word in a sentence. This method seems to disproportionately affect non-native English speakers’ writing, leading to inaccurate assessments of their work as being AI-generated.
The current AI detectors, particularly those targeting GPT-generated content, have a noticeable and concerning bias against non-native English speakers.
This issue underscores the need for further refinement and adjustment in AI detection tools to ensure fairness and accuracy, especially in a global context where English is not the first language for many users.
Are AI Content Detectors Accurate?
With existing AI detectors, things are taking a complex and unlikely turn.
Are AI content detectors accurate?
Despite the high claims of AI detectors being 97-99% accurate, no publicly available AI detectors are 100% accurate or reliable in practical scenarios.
Experts and educators raise ethical and pedagogical questions about AI in education and suggest its adoption with the education system to strategize modern learning.
About AI detectors? They still have a long way to prove themselves as they lack high variability of detection accuracy, neglect short texts, and don’t have a language specificity.
Claims By Leading AI Detectors
Originality AI touts a 99% accuracy rate, with under 2% false positives, in distinguishing AI-made text. They attribute their top-notch detection to a smart and masterful AI team and the ability to invest in more computing power, thanks to their pay-to-use model.
Copyleaks, meanwhile, claims an industry-leading false positive rate of just 0.2%. They credit their success to focusing on identifying human-written text, rather than specifically targeting AI-generated content.
The Future of AI Content Detection
AI-generated content is on the rise, and so are tools claiming to spot whether content is AI or human-made. But, finding a tool that’s spot-on at identifying both? That’s tough. The race is on between AI content creators and detectors, with AI like GPT-3 and GPT-4 setting high standards. AI detectors are lagging a bit for now.
Even so, these tools are pretty handy during content editing. They flag potential issues, making them useful before we publish anything.
We have run each piece through these 3 detectors to catch any snags but they don’t beat human insight, especially for SEO and fact-checking.